| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
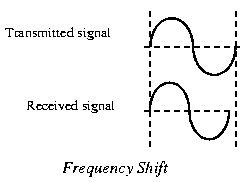
26c. Frequency Shift | Next |
Amplitude Jitter is the small constantly changing swings in the amplitude of a signal. It is principally caused by power supply noise (60 Hz) and ringing tone (20 Hz) on the signal.
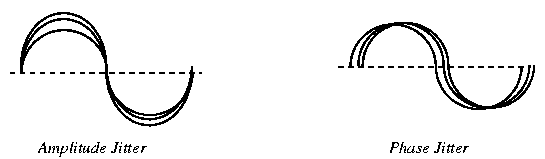
Phase Jitter is the small constantly changing swings in the phase of a signal. It may result in the pulses moving into time slots allocated other data pulses when used with Time Domain Multiplexing.
Telephone company standards call for no more than 10 degrees between 20 and 300 Hz and no more than 15 degrees between 4 and 20 Hz.
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |