| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
18a. Hardware Handshaking (cont'd) | Next |
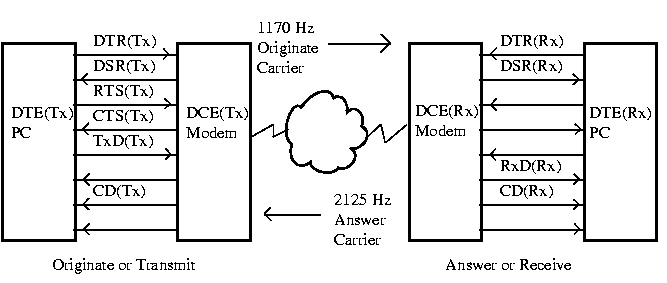
| a. | Modem sends CD(Tx) | - We're connected and they are sending us good carrier! |
| b. | PC sends RTS(Tx) | - Okay send them our carrier (1170 Hz). |
| c. | Modem waits | - Delay so that Rx modem can lock to the carrier |
| d. | Modem sets CTS(Tx) | - Okay now we should be ready to send data |
| e. | PC sends TxD(Tx) | - Here's some data to send over. |
4. At the Receive End:
| a. | Modem sends CD(Rx) | - We're connected & they're sending good carrier (1170 Hz |
| b. | Modem sends Rxd(Rx) | - Here's some data for you. |
The communication program then interprets the data and decides if a reply is required or if more data is coming. The communication programs handle the transfer of the data and the direction.
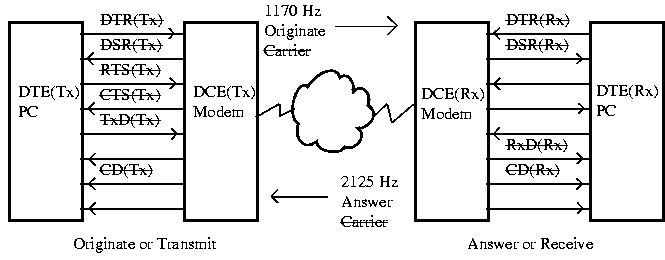
5. Both Originate or Answer can end the communication:
| a. | DTE(Tx) drops RTS(Tx) or DTR(Tx) | - I'm done, hang-up the phone. |
| b. | DCE(Tx) modem drops DSR(Tx) and the Carrier (1170 Hz) | - I've disconnected. |
| c. | DCE(Rx) modem drops CD(Rx) | - No carrier, they're hanging up |
| d. | DTE(Rx) drops RTS(Rx) | - Hang up on them |
| e. | DCE(Rx) modem drops DSR(Rx) and the Carrier (2125 Hz) | - I've disconnected. |
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |