|
Introduction to Data Communications
15. Transmission Media - Guided (cont'd)
15c. Coaxial Cable
Coaxial Cable consists of 2 conductors. The inner conductor is held inside
an insulator with the other conductor woven around it providing a shield. An
insulating protective coating called a jacket covers the outer conductor.
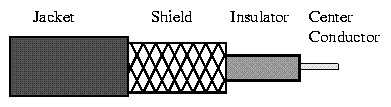
The outer shield protects the inner conductor from outside electrical signals.
The distance between the outer conductor (shield) and inner conductor plus the
type of material used for insulating the inner conductor determine the cable
properties or impedance. Typical impedances for coaxial cables are 75 ohms for
Cable TV, 50 ohms for Ethernet Thinnet and Thicknet. The excellent control of
the impedance characteristics of the cable allow higher data rates to be
transferred than Twisted Pair cable.
15d. Optical Fibre
Optical Fibre consists of thin glass fibres that can carry
information at frequencies in the visible light spectrum and beyond.
The typical optical fibre consists of a very narrow strand of glass
called the Core. Around the Core is a concentric layer of glass
called the Cladding. A typical Core diameter is 62.5 microns (1
micron = 10-6 meters). Typically Cladding has a diameter of 125
microns. Coating the cladding is a protective coating consisting of
plastic, it is called the Jacket.
|