| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
62c. X.25 Packet Formats | Next |
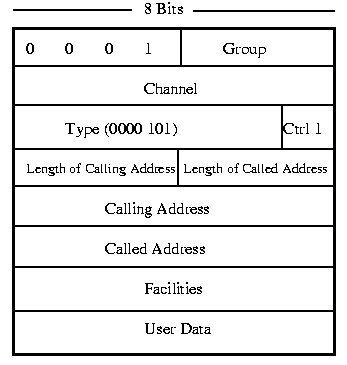
Call Request Frame
The Call Request Frame is used to initiate and setup the call from one X.25 service to another. After the call is established, the Call Request frame is not used.
Logical Channels
There are 4096 Logical Channels available on a single physical connection to an X.25 network. The Logical Channels are divided into Groups and Channels. There can be 16 groups (4 bits) of 256 channels (8 bits). 16 x 256 = 4096. The Logical Channel Numbers (LCN) are used to identify the connections to the Network.
Type Field:
For Call Request the Type Field is always equal to 0000 1011. Note the last bit is called the Control bit and is set to 1.
Length of Calling/Called Address:
The Length of Calling/Called Address allows different sizes of addresses for other protocols. The standard protocol is IP with an address length of 32 bits.
Calling/Called Address:
Only used during Call Connect until the Virtual Channel is established then the LCN (Logical Channel Numbers) are used to identify the connections.
Facilities Length
Indicates the length of the Facilities Field
Facilities Field
Indicates the types of facilities available. Facilities depend on the Network provider and can include information such as Charges or Call Forwarding.
Once a Call is established, The Calling/Called Addresses and Facilities Fields are not required and the Control Packet Format and Data Packet are used.
Control Frame
The Control Frame is used to control the communications during the call.
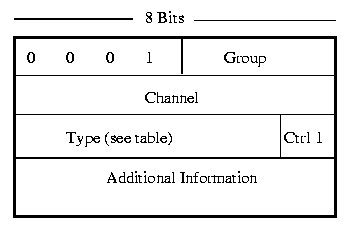
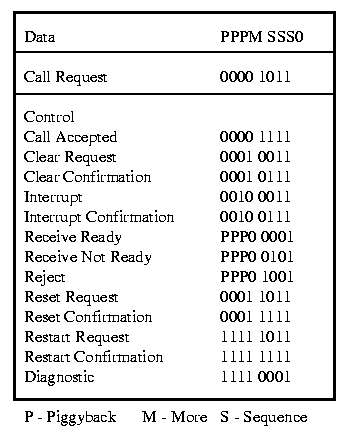
X.25 Type field table for all 3 packet types
The Data Frame is used to transfer data between destination and source.
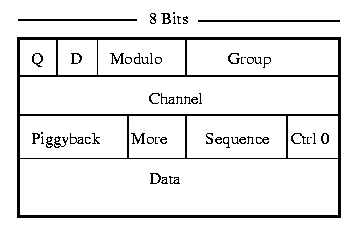
Q
Optional - Q is used to distinguish between data and control information.
D
D controls the type of Acknowledgment:
Modulo
It is used by the sliding window. The modulo allows multiple unacknowledged packets on the network for faster response. The modulo can be Modulo 8 or Modulo 128 (127 packets out on the network)
Piggyback
The Piggyback field is used for Acknowledgement with the Modulus (sliding window)
Sequence
The Sequence field holds a unique packet number which identifies the packet.
More
The More field indicates that more data is coming.
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |