| Introduction to Data Communications |
 Previous Previous
|
9. The Role of Telecommunications in Networking |
Next  |
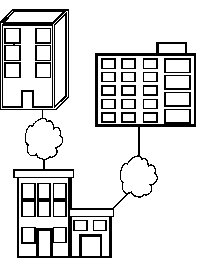
From The Big Picture, we see that telecommunications provides a connection service (storm clouds) between networks (circles). Telecommunications provides the external connection service for joining networks across cities, provinces and countries.
Local Area Networks - a system of computers that share resources such as hard-drives, printers, data, CPU power, fax/modem, applications, etc... They usually have distributed processing - means that there is many desktop computers distributed around the network and that there is no central processor machine (mainframe). Can be campus wide like a college or university.
 Location: In a building or individual rooms or floors of buildings or nearby buildings.
Location: In a building or individual rooms or floors of buildings or nearby buildings.
Metropolitan Area Networks: a system of LANs connected through out a city or metropolitan. MANs are used to connect to other LANs. A MAN has to have the requirement of using a telecommunication media such as Voice Channels or Data Channels. Branch offices are connected to head offices through MANs. Examples of companies that use MANs are
universities and colleges, grocery chains and banks.
 Location: Separate buildings distributed throughout a city.
Location: Separate buildings distributed throughout a city.
Wide Area Networks: a network system connecting cities,
countries, continents together. TransCanada Pipeline has a WAN
that stretches from Alberta to Boston. It goes from Alberta to
Ontario then through the States and ends up in Boston. The
maintenance and control of the network resides in Calgary.
WANs are connected together using one of the telecommunications
media.
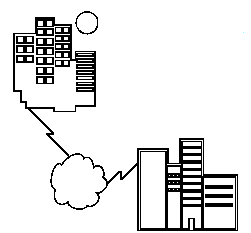 Location: City to city, across a country or across a continent.
Location: City to city, across a country or across a continent.
 Location: In a building or individual rooms or floors of buildings or nearby buildings.
Location: In a building or individual rooms or floors of buildings or nearby buildings.  Location: Separate buildings distributed throughout a city.
Location: Separate buildings distributed throughout a city. Location: City to city, across a country or across a continent.
Location: City to city, across a country or across a continent.