| Introduction to Data Communications |
 Previous Previous
|
7. Breaking The Big Picture up! (con'td) |
Next  |
 7b. LANs (cont'd)
7b. LANs (cont'd)
Examples of hardware devices are:
- Network Interface Cards NICs
- Repeaters
- Ethernet Hubs or multiport repeaters
- Token Ring MultiStation Access Units (MSAUs), Control Access Units (CAUs) and
Lobe Access Modules (LAMs)
- Bridges
- Brouters
- Routers
- Gateways
- Print servers
- File servers
- Switches
Examples of LAN protocols are:
- Ethernet frame types: Ethernet_II, Ethernet_SNAP, Ethernet_802.2, Ethernet_802.3
- Media Access Control layer (MAC layer)
- Token Ring: IBM and IEEE 802.5
- Logical Link Control Layer (LLC) IEEE 802.2
- TCP/IP
- SMB, NetBIOS and NetBeui
- IPX/SPX
- Fiber Distributed Data Interchange (FDDI)
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) are networks that connect LANs together within a city.
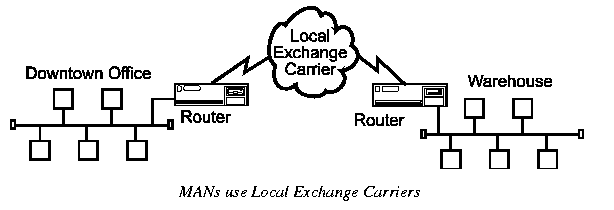
The main criteria for a MAN is that the connection between LANs is through a local exchange carrier (the local phone company). The protocols that are used for MANs are quite different from LANs except for ATM which can be used for both under certain conditions.
Examples of MAN protocols are:
- RS232, V35
- X.25 (56kbps), PADs
- Frame Relay (up to 45 Mbps), FRADs
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) PRI and BRI
- Dedicated T1 lines (1.544 Mbps) and Fractional T1
- T3 (45 Mbps) and OC3 lines (155 Mbps)
- ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line) up to 8 Mbps
- xDSL (many different types of Digital Subscriber Lines)
