| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
41d. Bridge Methodologies | Next |
Transparent Bridges were originally developed to support the connection of Ethernet networks. The spanning tree protocol was developed to improve upon transparent bridging. Source Routing Bridges are used by Token Ring. Source routing bridges require a solid understanding of Token Ring concepts and as such will be covered under the section discussing Token Ring.
Transparent Bridges
Transparent Bridges examine the MAC address of the frames to determine whether the packet is on the local Segment or on the distant Segment. Early bridges required the system administrator to manually build the routing table to tell a bridge which addresses were on which side of the bridge. Manually building a routing table is called fixed or static routing. Modern bridges are self-learning, they listen to the network frame source addresses to determine which side of the bridge the node is on and build a routing table that way.
The following network will be used as an example of a self-learning transparent bridge's routing table construction.
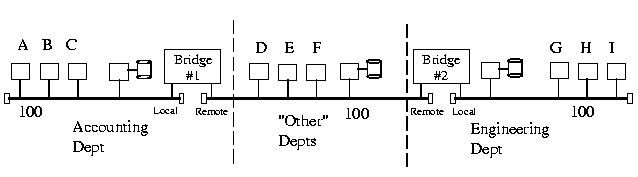
As frames flow on Bridge #1's local port, Bridge #1 examines the source address of each frame. Eventually after all nodes on the local port, have become active, Bridge #1 associates their address as being on the local port. Any frames with a destination address other than the nodes on the local port are forwarded to the remote port. As far as Bridge #1 is concerned, nodes on Bridge #2's local port appear as if they were on Bridge #1's remote port.
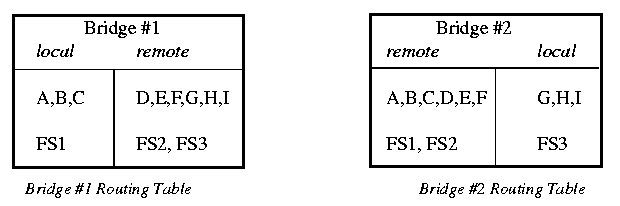
Bridge #2 builds its routing table in a similar manner to Bridge #1. Note the differences.
| Introduction to Data Communications | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
Table of Contents | Next |